What is Balkanization
There have been numerous historical instances where a major sovereign state has split up. When a sovereign state divides or fragments into a smaller, often ethnically similar nation, this practice is called Balkanization. The definition of this separation was initially documented in the early 19th century. It refers to the breakup of the Balkan Peninsula. This state was led by the Ottoman Empire and soon broke off into several smaller states between 1817 and 1912. Due to the activities of World War I, many states began to use this term more commonly. Many new states emerged due to the fall of the Austro-Hungarian Empire and the Ottoman Empire. Balkanization often occurs due to differences in ethnicity, culture, and religion. Groups seek sovereignty to protect their beliefs regarding nationalism, independence, imperialism, and anti-colonialism.
Balkanization Example
Southern Africa, West Africa and British East Africa are some significant examples of Balkanization that took place from the 1960s – 1980s. The countries in these areas were subjects of the Communauté Financière Africaine and the British government.
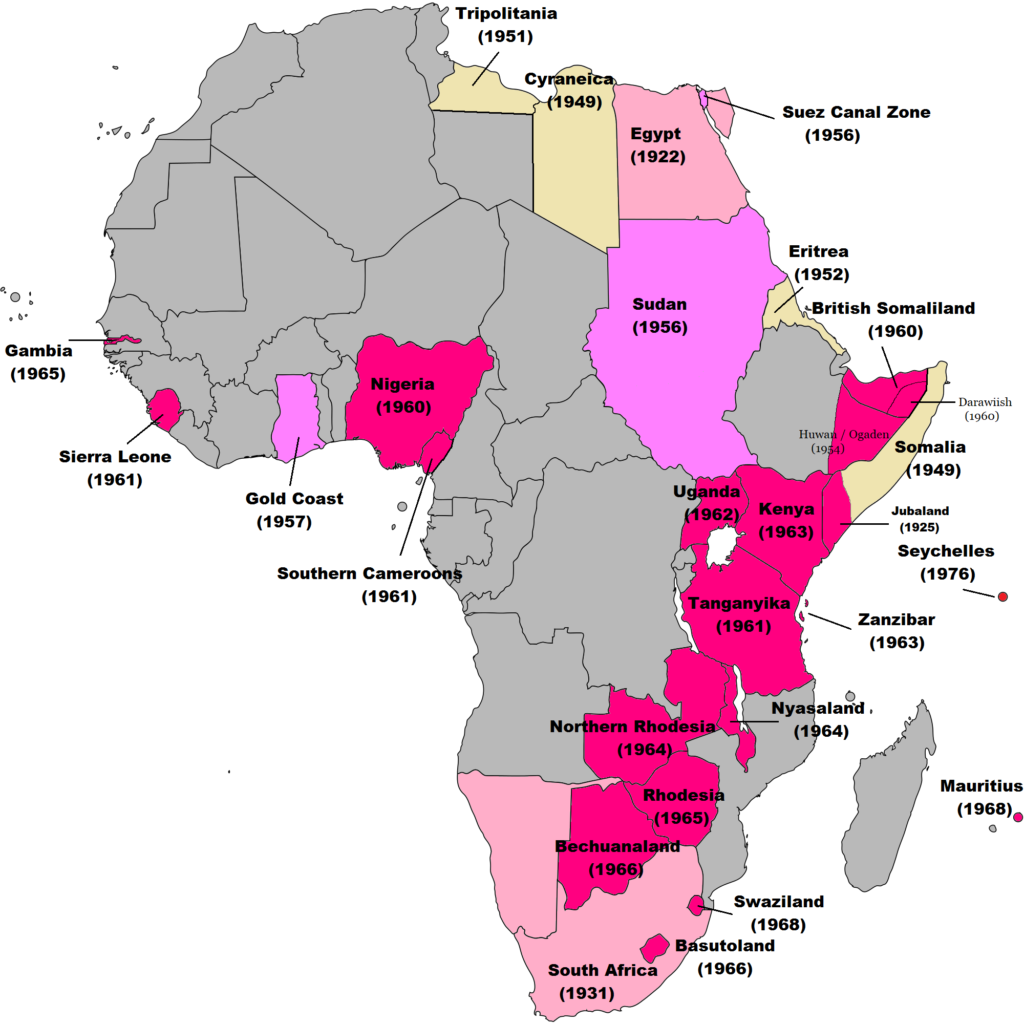
Zambia, Zimbabwe, Malawi, Uganda and Tanzania sought sovereign autonomy from their colonizers. Through diplomatic endeavours and an armed struggle, they managed to achieve independence. This action meant that the Great Powers became smaller and led to the postcolonial era. Balkanization of the British and French empires meant a breakdown of the Federation of the Rhodesias and Nyasaland. Many smaller independent countries emerged from the boundaries drafted by their former colonial masters. These newly sovereign nations were originally splinters of a closed economy. The initial process of Balkanization can lead to poor economic conditions. Without the former’ mother state’s administrative, financial and human resources, it can be difficult for balkanized splinter states to subsidize their local industries. It led to the introduction of antitrade and anti-market policies from colonizer nations which closed off the countries through sanctions and meant the interior markets were small in scale. Due to many of these states being under one government, the transport networks became fragmented after Balkanization. Labour and capital flow regulations were increased, making free trade difficult. Changes in policy and leadership meant new barriers were introduced across Africa between 1960 and 1990.
Balkanization of America
The social dynamics in diversity within the U.S. have led to commentary and social science research that predicts the potential Balkanization of the country. Numerous geographical trends in contemporary U.S. societies could lead to the request for sovereignty. This phenomenon is described as “demographic balkanization”. It is a term used to reference a spatial segmentation of the population. The groups are often restricted through race-ethnicity, class, and age. When these societies grow and feel underrepresented by lawmakers, their differences can sprout across broad regions, states, and metropolitan areas. The state of immigration and long-distance internal migration patterns within the U.S. are significant factors. Balkanization as a result of immigration-driven ethnic fragmentation in the U.S occurs to prevent ethnic territorial conflict. The U.S. has become divided, and with the intensification of profoundly negative perceptions of current immigration, Balkanization is possible. An immigrant-induced nation breakup has happened before in history within the country of Yugoslavia. Unified nations with a common demographic culture can often defeat normative and defective assumptions about space and immigrant assimilation. The prospect of the U.S. is an image that directs future research and social policy. The combination of gerrymandering and poor immigrant representation shows a lack of neutrality, leading to Balkanization.
Difference between Devolution and Balkanization
Balkanization differs from devolution as it involves a total separation from nationalism, independence, imperialism, and anti-colonialism. This complete breaking up of a country results in a sovereign state dividing into a smaller nation. Devolution is a significantly less aggressive transfer of power. This method gives authority to quasi-autonomous units of local government with corporate status. It is only the movement of power from a centralized point to a more regional scale. The critical point surrounding devolution is that this move can eventually lead to the Balkanization of a state.
Similarities between Devolution and Balkanization
- As states rise and declare their ability to manage their affairs independently, it can lead to devolution and then Balkanization.
- Devolution is a tool that can cause Balkanization. It can also occur as a direct result of Balkanization.
- Devolution is a widespread practice for unitary governments that wish to improve their administrative capacity. This practice is similar to Balkanization as these independent breakout societies want to handle the administration of their demographics. Both methods involve transferring power to lower levels of government/society.
Example of Devolution
Devolution involves placing administrative decision-making, finance, and management in the hands of local citizens. An example of this is municipalities electing their mayors and councils. These selected leaders are then given the mandate to raise revenues for development. The central government still supervises these individuals; however, they have the independence to invest the public funds accordingly. This authority is granted to them within the geographical boundaries of the central government.
Is Balkanization good?
The separation of states from countries in smaller regions often reduces the need for people to be associated with others they do not wish to be. Balkanization can be a good thing if there is a logically defined limit. Without forceful integration, there is likely to be less conflict. These ‘divorces’ are not always chaotic and problematic but logical. If there is a responsible party that causes hostilities, leading to division, then separation can be a positive aspect. Where groups of society are misrepresented and denied political and human freedoms, they are likely to support the division. Freedom of association is guaranteed by the constitution, allowing the right to disassociate as well. Oppression and mistreatment are critical factors in Balkanization. Citizens who support this will argue that getting away from their oppressors cannot be an adverse action.
Balkanization can be done diplomatically, allowing for minimal hostility and violence. The social relations between countries can remain intact regardless of this division process.






































